
In preliminary research by our group, the compressed aluminium pieces were immersed in a colloidal solution of zirconium, and evidence of wear resistance was reported Citation9. Studies on aluminium MMCs synthesised with nanosized dispersions of mullite and zirconia through uniaxial hot-pressing at temperatures in the range of 450–610☌ showed that the values of dislocation density increased with temperature Citation8. Aluminium–matrix composites containing nanometre-sized particles of zirconia were prepared by the hot pressing technique, showing an increase in hardness Citation7. There are few investigations of aluminium–matrix-based composites with reinforcement of zirconia, which has low adhesion to aluminium, Therefore, the processing of powder metals shows advantages over conventional methods of casting. A nanocrrystalline ZrO 2/Al composite has been fabricated by the squeeze casting route using specially designed casting equipment Citation6. Aluminium–matrix-based composites have exhibited further improvement in the mechanical properties of ceramic particulates. Accordingly, in the last few years, aluminium matrix composites have been utilised in high-tech structural and functional applications including aerospace, defense, automotive and thermal management areas, as well as in sport and recreation Citation4.įrom the industrial standpoint, it is advantageous to fabricate metal matrix-particulate composites using powder metallurgy because the fabricated composites possess a higher dislocation density, a small sub-grain size and limited segregation of particles Citation5. Aluminium-based MMCs can provide excellent wear resistance, provided the possible limitations of the benefits of reinforcement are appreciated Citation3.

A method to improve wear resistance is by forming a particle-dispersed alloy. A slight change in these factors sometimes causes a big difference in wear Citation2. The wear resistance depends largely on the nature of the wearing surface and on the rubbing condition. Moreover, prediction of wear is difficult because it is not an intrinsic property of the material but rather a function of the system. However, the wear resistance of aluminium is low in dry sliding. Silicon carbide and alumina are amongst the most common ceramic particles for this purpose.Īluminium is a very attractive metal matrix for a number of technical and economical reasons. The wear behaviour of MMCs depends on the nature of particle reinforcement and on the nature of the matrix containing them. Synthesis techniques in these cases include powder metallurgy, mechanical alloying, squeeze casting, stir casting, compocasting and low-pressure infiltration, among others. Normally, particulate-reinforced composites cost less than fibre reinforcement composites Citation1. These interesting materials generally consist of a metal matrix in which non-metallic fibres, particles or whiskers are dispersed. These will jump to the rightmost slot as they are filled.īe patient when using the Squeezer, as it will take some time to even start to fill up the liquid meter.Metal–matrix composites (MMCs) are increasingly attracting interest because of their superior mechanical and tribological properties. In the leftmost of these, you place empty cans the liquid is collected into.
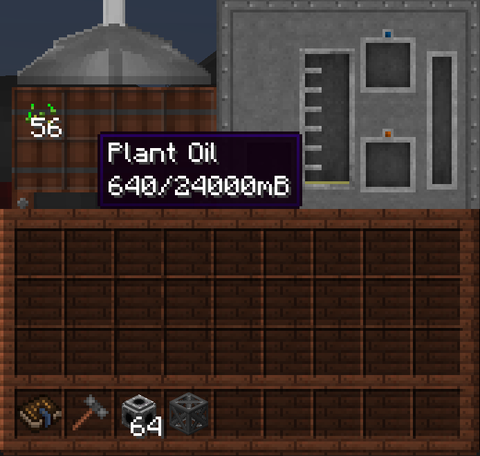

The Squeezer UI has a 3x3 grid to the left where you can place ingredients to be squeezed, a meter showing how much liquid has been produced, and two slots in the bottom right.
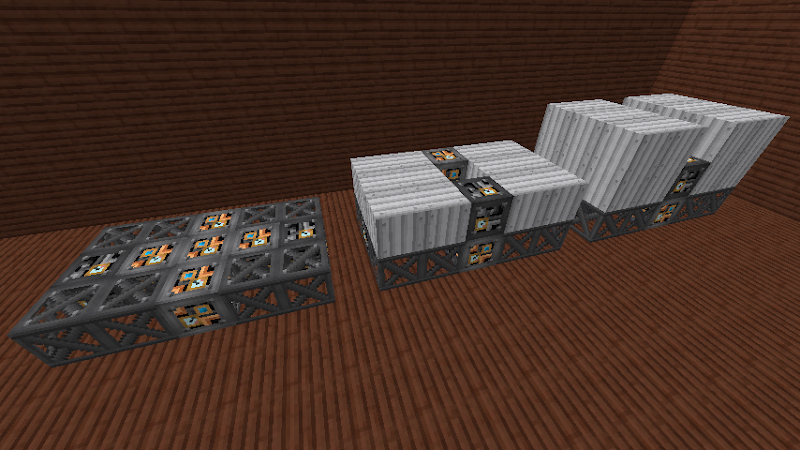

The squeezer has outputs on the side, item input in the front, and power input from the back. However, the Squeezer will work with Redstone Flux (RF) power as well. It does however reach its maximum speed at approximately 5MJ/t. The more power provided to the Squeezer the faster it will run.
INDUSTRIAL SQUEEZER IMMERSIVE ENGINEERING MOD
The Squeezer is a machine added by the Forestry Mod to squeeze liquids and other materials out of objects.Īs with all other Forestry machines the Squeezer will work as a power sink in a Buildcraft power network as long as it has work to do.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
